As a child, Xiaowei Zhuang was encouraged to question the physical relationships between objects she saw in the world around her. Xiaowei and her brother were prompted with quizzes from their father—a physics professor—to consider what forces were present in a glass of water on their kitchen table. Her father’s questions—and his subsequent enthusiasm for Xiaowei’s answers—inspired Xiaowei’s lifelong curiosity to understand relationships between objects in the natural world and how we see them.
Human beings—they’re really visual animals. Seeing is believing.
“Of course, there are a lot of things in nature that are hard to see, especially when you get to the molecular level,” says Xiaowei.

Propelled by her curiosity and passion for understanding the unseen in the physical world, Xiaowei completed her undergraduate degree in physics at the University of Science and Technology in China. At the age of 19, she emigrated to the United States to pursue her doctorate under the mentorship of Yuen-Ron Shen at the University of California, Berkeley. Xiaowei’s travel from China to the United States marked both her first flight and travel away from home and the beginning of her prolific research and academic career. At Berkeley, her doctoral research focused on the physics of interfaces using nonlinear optics, studying how liquid crystals interact with solid surfaces, with implications on image display in LCD technologies.

In 1997, she pursued a Chodorow Postdoctoral Fellowship at Stanford under the mentorship of physicist Steven Chu—who would win a Nobel Prize that year for his work using lasers to study atoms. At Stanford, Xiaowei applied her passion for imaging and the physics of light to the use and development of bioimaging techniques. It was in there that Xiaowei first used a technique known as single molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) to highlight and thus visualize the structures and dynamics of RNA enzymes. These studies enabled previously intractable questions to be answered; Xiaowei understood that being able to observe RNA at the single-molecule level allowed scientists to identify transient intermediates produced while molecules were undergoing structural changes, stating that “with single molecule techniques we can capture these structural dynamics in real time—and then understand how they influence function.”
In 2001, Xiaowei applied for faculty positions at seven schools and received offers from all of them. She accepted a position at Harvard as an assistant professor of chemistry and chemical biology and of physics, noting that it was her interactions with her potential future colleagues during the interview process that compelled her choice. “The interactions and conversations were just so much fun,” she said, and “they were genuinely interested in what I do, rather than just think of what I do as high-quality work.”
At Harvard, Xiaowei set to work in developing tools to overcome the diffraction barrier, which had stymied researchers from being able to view biological cells and tissues at high resolution. Applying her interest and profound understanding of the physical properties of light, she developed a new super-resolution imaging technique called STORM—stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy. STORM engages the application of light-switchable dyes to target molecules in cells and render them visible, allowing scientists to see the detailed structures within cells at a resolution and with a clarity never previously possible—including the periodic skeletal structures in neurons. This outcome had a powerful impact on Xiaowei: “It’s just a really remarkable feeling,” she said, “a discovery of something that people never knew existed before.”
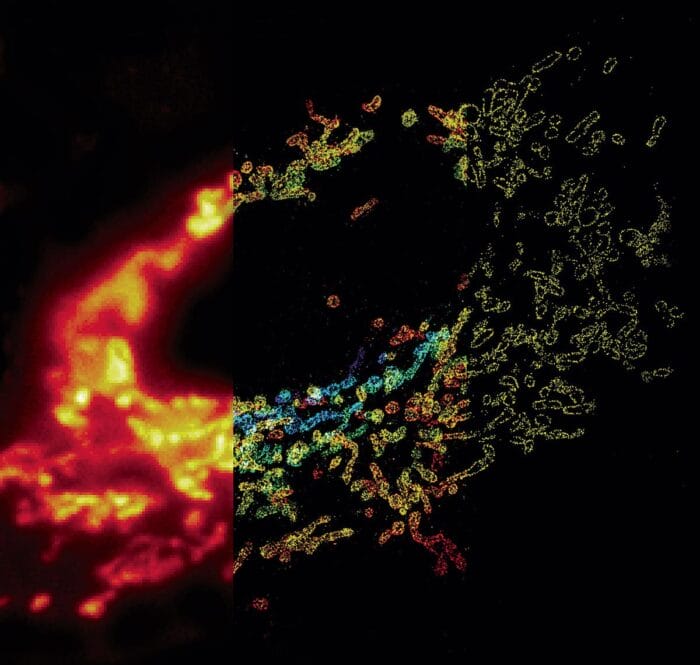
Following the success of STORM, Xiaowei pioneered another imaging technology with applications to visualize and quantify RNA molecules at the genome scale—multiplexed error-robust fluorescent in situ hybridization, or MERFISH. The technology allows researchers to develop a quantitative molecular catalogue to describe different cell types and their spatial organization in the human body—and has become a primary tool used by researchers with the Human Cell Atlas Project.

The importance of community and human relationships to Xiaowei’s work is evident—from her earliest conversations with her father to the mentorships and partnerships that have inspired her throughout her astounding career. A core value of the Vilcek Foundation is our understanding that diversity in thought and discourse compel discovery and further growth.
“People who grow up in a different culture—they think differently—they have a different approach to things,” notes Xiaowei. “It’s the best way to advance science.”
Related News
Shixin Liu: “Seeing is believing”

Vilcek Foundation honors immigrant scientists with $250,000 in prizes

Biophysicist Ibrahim Cissé receives prestigious MacArthur Fellowship

You may also be interested in
Shixin Liu

Ibrahim Cissé

Xiaowei Zhuang
